How AI Is Redefining Competencies in Europe’s Labour Market
July 31st, 2025
Introduction
Artificial intelligence continues to integrate deeply into European workplaces, fundamentally tweaking the usual skills that are demanded by employers. As businesses increasingly rely on AI-powered technologies, workers are expected to evolve their technical capabilities and essential interpersonal skills to stand out in today’s rigorous job market.
This comprehensive analysis titled, Skill Demand in the Age of AI: Evidence from Europe by Najada Feimi, Christina Gathmann, Terry Gregory, and David Marguerit, draws upon over 33 million online job postings from Belgium, France, Germany, and Luxembourg between 2018 and 2022, providing strong empirical evidence showing how much influence AI exposure is having on occupational skill requirements, workforce policies and training initiatives.
The Challenge of This Research
Understanding the growing demand for skills in this AI era involves several significant challenges:
- Scale and diversity: Extracting and standardizing explicit skill mentions from an extensive multilingual dataset of more than 33 million job postings written in French, German, Dutch, and English.
- Consistent classification: Developing a systematic classification method capable of accurately grouping millions of unique skill descriptors into seven distinct categories relevant to workforce development.
- Measuring AI Exposure: Constructing a precise and dynamic measure of occupational AI exposure by linking real-world AI coding activity, sourced from developer platforms like Stack Overflow, directly to occupational skillsets.
The MeluXina Solution
To address these complex challenges, the researchers relied on MeluXina’s advanced computational capabilities to:
- Integrate Massive Datasets:
Processed over 33,000,000 unique job advertisements from national and international job portals, to ensure extensive geographic and occupational coverage across Belgium, France, Germany, and Luxembourg.
- Perform Multilingual Skill Extraction:
Executed advanced multilingual large language models (LLMs), Mixtral AI, which automatically detected and collated skill mentions across diverse terminology and language variants. This led to the achievement of approximately 85% extraction accuracy, largely outperforming conventional keyword-based methods.
- Classify Skills Using AI Models:
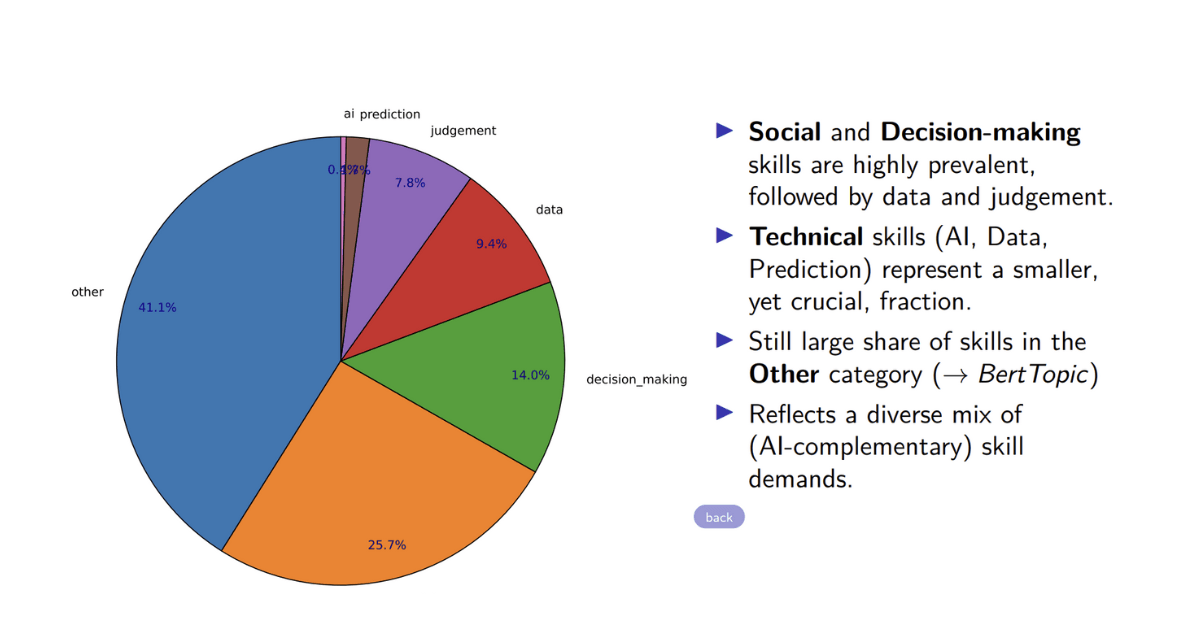
Implemented supervised neural network classifiers, trained on manually labelled subsets of around 500 skills, and successfully categorized extracted skills into seven key clusters: AI, Data, Prediction, Judgement, Decision-Making, Social, and Leadership, with classification accuracy exceeding 85%.
- Develop a Dynamic Occupational AI Exposure Index:
Created an innovative metric by correlating Stack Overflow query volumes for AI-related programming tags (e.g. “machine-learning”, “deep-learning”) with occupational skill profiles, which resulted in an annually adjusted AI exposure score for over 400 occupations, enabling precise quantification of AI’s impact on job requirements.
The Impact
MeluXina’s computational power was highly evident, yielding critical insights with significant implications, as follows:
- Substantial Growth in Technical Skills:
Jobs with higher AI exposure saw demand rise up for specialist skills in artificial intelligence, prediction, and data. For example, job postings for professionals are 15 percentage points more likely to require data skills compared to those for sales and marketing roles
- Rapid Expansion of Complementary Skills:
Jobs with higher AI exposure show greater demand for complementary skills like judgment, decision-making, and social abilities. For instance, professional roles are 16.3 percentage points more likely to require decision-making skills than sales and marketing jobs.
- AI Exposure Reduces Skill Concentration Across Occupations:
Occupations with higher AI exposure tend to require a more diverse skill set, as reflected in a lower Herfindahl Index of skill concentration. This includes both technical and complementary human skills.
- Informative Policy Insights for Workforce Development:
These findings emphasise the urgency for strategic vocational training, lifelong learning programmes, and inclusive skill-development policies, especially for lower-skilled workers at higher risk of displacement due to AI adoption.

Conclusion
By leveraging MeluXina’s advanced computing capabilities, this study provided unprecedented insights into how AI adoption is reforming the skill requirements across Europe’s labour market.
These detailed, data-driven findings, powered by MeluXina, equip policymakers, educators, and industry leaders with robust information to anticipate skill gaps and proactively develop strategies, ensuring the European workforce remains resilient, adaptable, and competitive in an increasingly AI-driven economy.


